In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain technology, scalability remains one of the most pressing challenges․ Enter Celestia, a groundbreaking solution designed to address this issue and revolutionize the way we think about blockchain architecture․ This article delves into what Celestia is, how it works, and its potential to unlock blockchain scalability for various applications․
What is Celestia?
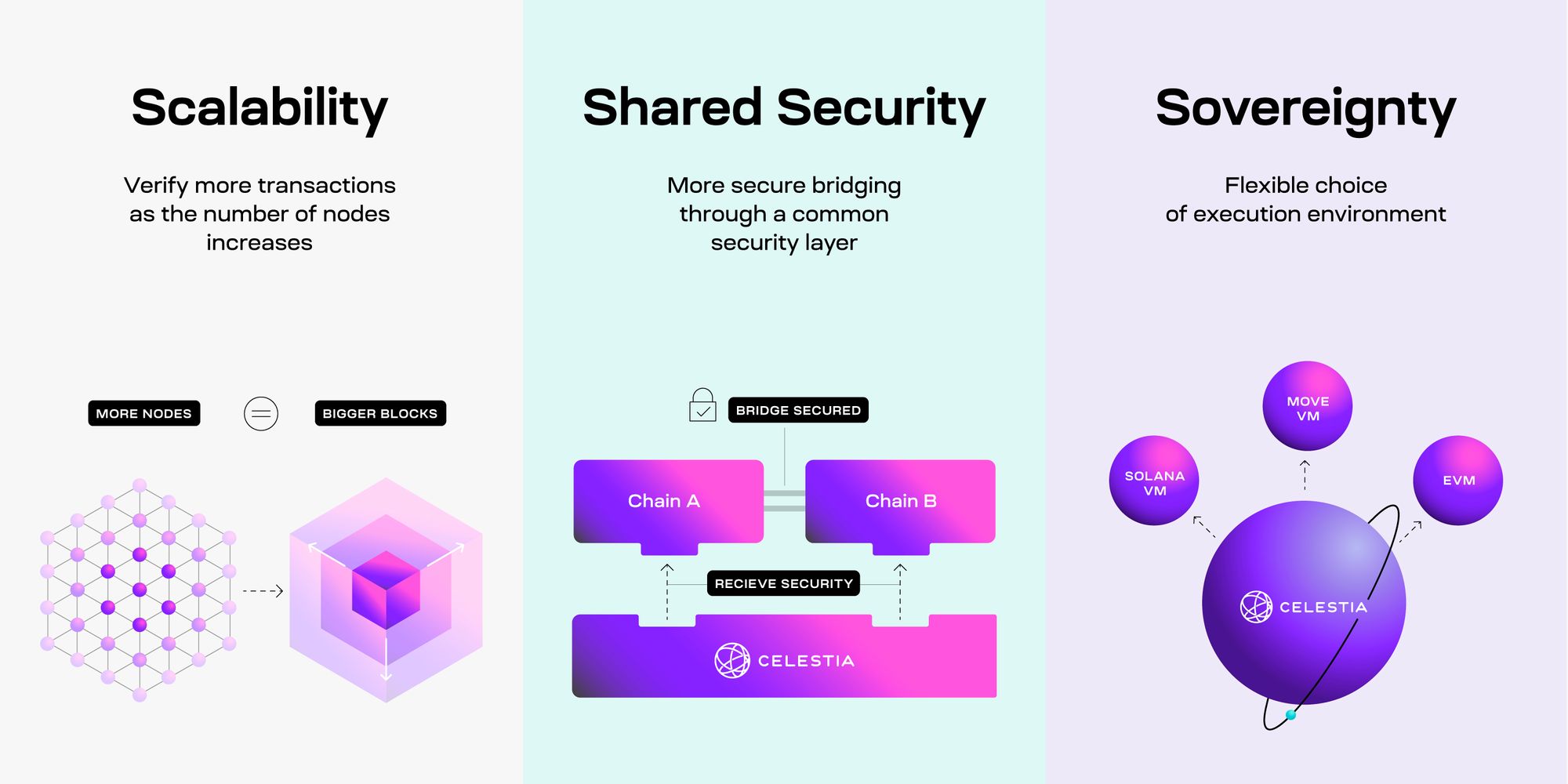
Celestia is a modular blockchain network that separates consensus and data availability from execution․ This innovative approach allows for greater scalability and flexibility, enabling developers to build and deploy their own blockchains without the need to reinvent the wheel․ By decoupling these layers, Celestia provides a platform that can support a wide range of decentralized applications (dApps) while ensuring security and efficiency․
Key Features of Celestia
- Modular Architecture: Celestia’s design allows different components of the blockchain to operate independently, which helps in optimizing performance and scalability․
- Data Availability: Celestia ensures that data is available to all participants in the network, which is crucial for maintaining security and trust․
- Customizable Rollups: Developers can create their own rollups that utilize Celestia’s infrastructure, allowing for tailored solutions to specific use cases․
- Interoperability: Celestia facilitates interaction between various blockchains, enhancing the overall ecosystem and enabling cross-chain functionalities․
How Does Celestia Work?
Celestia operates on a unique consensus mechanism that combines Proof-of-Stake (PoS) with a custom-designed data availability layer․ Here’s a breakdown of its core functionality:
1․ Consensus Layer
The consensus layer in Celestia is responsible for validating transactions and ensuring that they are agreed upon by the network participants․ By utilizing PoS, Celestia provides a secure and energy-efficient way to reach consensus without the high costs associated with Proof-of-Work (PoW) systems․
2․ Data Availability Layer
This layer ensures that all data related to transactions is available for verification․ Celestia employs sophisticated mechanisms to ensure that even in the case of network partitions, data remains accessible, which is critical for maintaining the integrity of the blockchain․
3․ Execution Layer
The execution layer is where smart contracts and dApps operate․ By allowing developers to build their own execution environments, Celestia provides the flexibility needed to adapt to various application requirements․ This layer can handle different programming languages and execution models, making it versatile for developers․
Benefits of Celestia for Scalability
Celestia’s innovative approach to blockchain architecture offers several benefits that can significantly enhance scalability:
- Increased Throughput: By separating execution from consensus, Celestia can handle a much larger number of transactions simultaneously, reducing bottlenecks․
- Lower Transaction Costs: The modular design allows for optimized transaction processing, leading to reduced fees for users․
- Flexible Development: Developers can quickly prototype and deploy new dApps without the overhead of building a full blockchain from scratch․
- Decentralized Infrastructure: Celestia encourages a decentralized ecosystem where multiple blockchains can coexist and interact, fostering innovation․
Use Cases for Celestia
Celestia’s scalability solutions open the door to a variety of use cases:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): With lower transaction costs and increased throughput, DeFi applications can become more efficient and user-friendly․
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Artists and creators can mint and trade NFTs without facing high fees and slow transaction times․
- Gaming: Blockchain games can benefit from rapid transaction processing, enabling smoother gameplay and real-time interactions․
- Supply Chain Management: Companies can utilize Celestia for transparent and efficient tracking of goods through the supply chain․
Celestia represents a significant leap forward in the quest for blockchain scalability․ By decoupling the core components of blockchain technology, it allows developers to create highly efficient and customizable solutions that can cater to diverse needs․ As the blockchain ecosystem continues to grow, innovations like Celestia will play a crucial role in shaping its future․ In a world where speed, efficiency, and lower costs are paramount, Celestia stands poised to unlock the full potential of blockchain technology․
Future Prospects for Celestia
As Celestia continues to develop and gain traction, its future looks promising․ The modular architecture it employs not only addresses current scalability issues but also paves the way for future advancements in blockchain technology․ Here are some anticipated developments and trends that could shape Celestia’s trajectory:
1․ Enhanced Ecosystem Partnerships
As more developers recognize the advantages of Celestia’s architecture, we can expect a surge in partnerships and collaborations․ Projects that aim to leverage Celestia’s infrastructure will likely emerge, leading to a diverse array of applications across industries․ This collaborative ecosystem will drive innovation and enhance the overall usability of blockchain technology․
2․ Evolution of Governance Models
With the rise of decentralized networks, governance models will become increasingly important․ Celestia’s community-driven approach can lead to new governance mechanisms that enable stakeholders to have a more significant influence on the platform’s future․ This could involve decentralized voting systems or consensus-driven decision-making processes that foster inclusivity․
3․ Adoption in Enterprise Solutions
As businesses seek to integrate blockchain solutions into their operations, Celestia’s scalability and flexibility make it an attractive option for enterprise-grade applications․ Industries such as finance, healthcare, and logistics may adopt Celestia to streamline processes, enhance security, and reduce costs, driving mainstream acceptance of blockchain technology․
4․ Continued Research and Development
The Celestia team is likely to invest in ongoing research to enhance its technology further․ This may include exploring advancements in cryptographic methods, improving data availability techniques, and optimizing performance metrics, ensuring that Celestia remains at the forefront of blockchain innovation․
Challenges Ahead
While Celestia presents an exciting opportunity for scalability in blockchain, it is not without its challenges:
- Adoption Hurdles: Convincing developers and businesses to transition to a new architecture can be difficult, particularly when existing solutions already serve their needs․
- Security Concerns: As with any blockchain solution, ensuring the security of the network is paramount․ Celestia must continuously address potential vulnerabilities and threats․
- Market Competition: The blockchain space is becoming increasingly crowded, with numerous projects vying for attention․ Celestia will need to distinguish itself and continuously innovate to maintain its competitive edge․
Celestia represents a revolutionary approach to solving one of the most critical challenges in the blockchain domain: scalability․ By breaking down traditional blockchain structures into modular components, it empowers developers to create tailored solutions that are both efficient and adaptable․ As the demand for scalable blockchain solutions continues to grow, Celestia stands ready to lead the charge․ With ongoing developments, potential partnerships, and a focus on innovation, Celestia may very well reshape the landscape of decentralized technology for years to come․
As blockchain enthusiasts and developers look toward the future, keeping an eye on Celestia will be essential․ Its impact could define the next generation of blockchain applications, making scalability a reality rather than an elusive goal․ As the adoption of blockchain technology increases, Celestia’s role as a facilitator of this growth will likely be pivotal in unlocking the full potential of decentralized systems․